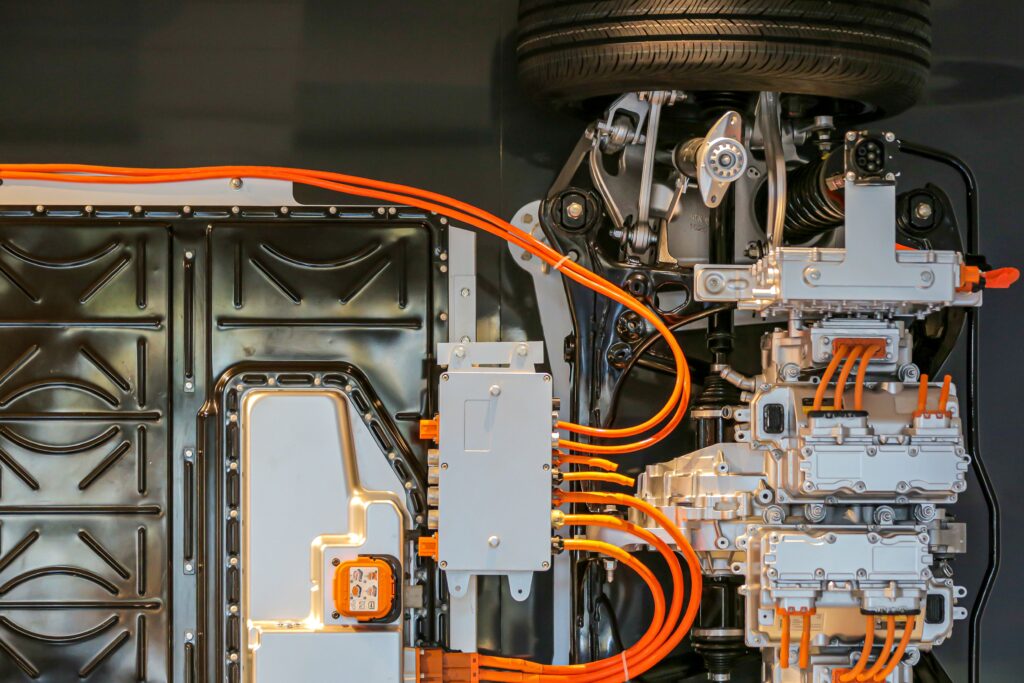
Cable & Wire Harnesses, Electronics
Wired for Success: The Intricate World of Wiring Harnesses from Design to Deployment
Wiring harnesses, intricate yet essential components of modern technology, play a crucial role across various industries. Let’s explore their journey from design to production, highlighting their connection types and wire varieties, and examining the industries that rely on them.
The Genesis: Design
Our story begins in the realm of design. Engineers and designers collaborate, using advanced software tools to create detailed blueprints. These blueprints define the exact layout, dimensions, and electrical requirements of the harness. The focus is on optimizing space, reducing weight, and ensuring the harness can withstand environmental factors like temperature fluctuations or vibrations.
Materials: The Building Blocks
The primary material in a wiring harness is the wire itself. Copper, known for its excellent conductivity and flexibility, is the most common choice. However, aluminum and silver are occasionally used for specialized applications. The wires are insulated with materials like PVC, rubber, or Teflon, depending on the harness’s intended use and required durability.
The Core: Types of Wires and Cables
In these harnesses, various types of wires and cables come into play. There are standard wires for basic electrical connectivity, twisted pairs for data transmission, and coaxial cables for high-frequency applications. Multi-conductor cables, often shielded, are used for more complex circuits.
Connection Types: Bringing It All Together
Connectors are the unsung heroes in wiring harnesses, ensuring reliable and secure connections. These range from simple plug-and-play connectors to sophisticated, waterproof, and locking types. There are also ribbon cable connectors for data and communication applications, and terminal blocks for industrial environments.
Production: From Design to Reality
The production of wiring harnesses is a blend of automation and skilled manual work. Automated machines cut, strip, and crimp wires with precision. Manual assembly is then required to route wires through sleeves, secure them with ties, and connect them to their respective terminals. Quality control is paramount, with rigorous testing for electrical functionality and durability.
Industries: The Lifeblood of Technology
Numerous industries depend on wiring harnesses. In automotive manufacturing, they are the nervous system of vehicles, connecting sensors, controls, and power sources. The aerospace industry requires them for complex avionic systems. Consumer electronics, home appliances, and computing hardware are everyday examples of harness usage. Industrial machinery, medical equipment, and even renewable energy systems also rely heavily on these intricate networks of wires.
The Evolution: Ongoing Innovation
As technology evolves, so do wiring harnesses. The advent of electric vehicles and the growing demand for renewable energy sources are pushing the boundaries of harness design and materials. The integration of smart technology and the need for lighter, more efficient harnesses drive ongoing innovation in this field.
In conclusion, wiring harnesses, though often unseen, are fundamental to the functioning of a vast array of technologies. From their meticulous design to their diverse applications, they exemplify the synergy of engineering and practical application, continuously adapting to meet the evolving demands of modern industries.